TL;DR: Content Delivery Network (CDN) ensures fast and reliable site delivery to every user, no matter where the user is located. It enhances speed and also helps boost Core Web Vitals and SEO signals. Know what CDN is and how you can achieve the benefits of it for your website.
People enjoy scrolling and browsing the internet a lot nowadays, so speed has become more important than ever. People expect websites to load within a few seconds, and search engines prioritize loading speed for higher rankings.
A CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a strong technology that makes websites fast, reliable, and scalable across different locations. But a lot of website owners are still not aware of its use and importance.
The efficient use can handle the traffic spikes and help improve the speed and overall performance of the site.
What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
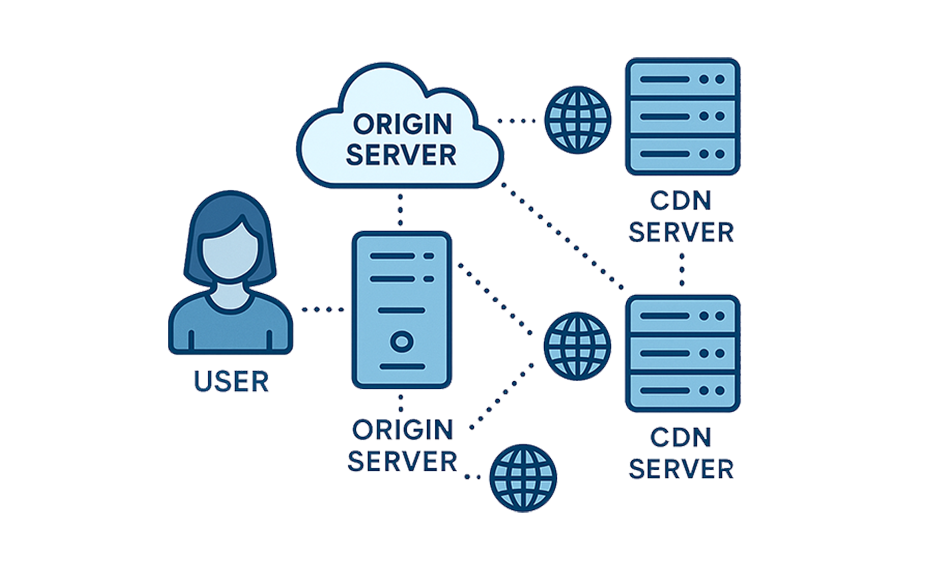
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a group of servers that are spread out over the world and positioned at strategic locations to speed up the delivery of content, including photos, videos, scripts, and web pages, to users.
A CDN serves cached content from edge servers, while still occasionally fetching from the origin if the cache is missing or expired. This implies that if your website is hosted in the US, someone from India doesn’t have to wait for the data to travel halfway around the world. Instead, the content comes from a server in Asia that is close by.
So, basically, it is a technique that uses a global server to deliver content, lower latency, handle the traffic efficiently, and speed up websites.
What Does a CDN Do?
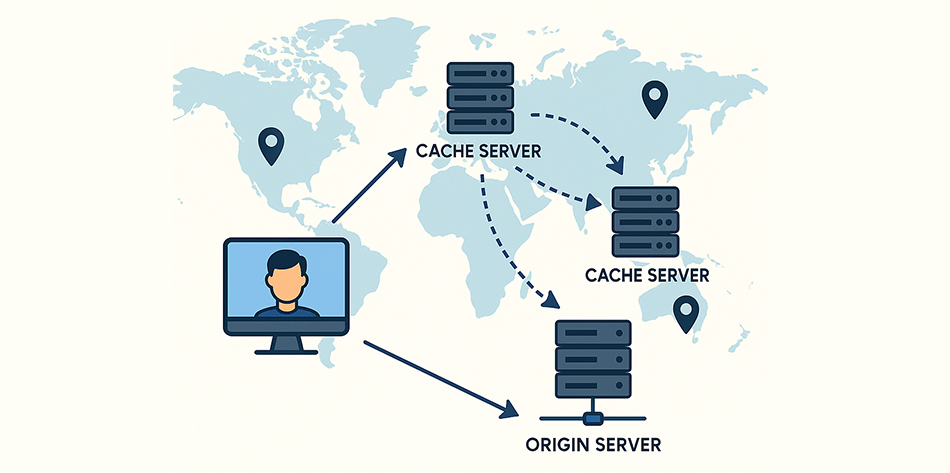
The network speeds up your website by providing data from the closest server to each visitor. Here’s how it works.
1. Cache Content
- A CDN keeps copies of your website’s static material (such as photos, CSS, and JavaScript files) on several servers across the world.
- This caching cuts down on the number of times you have to ask the origin server for the same thing, which speeds up load times a lot.
2. Edge Servers
These servers are located in important places on the worldwide server network. When a user asks for a webpage, the CDN routes them to the nearest edge server to speed up the delivery of the website.
3. Balancing the Load
A Content Delivery Network sends incoming traffic to several servers so that a single server doesn’t get overloaded, enhancing fast and efficient access.
4. Layers of security
Some CDNs include built-in security features such as DDoS mitigation, WAF, and SSL acceleration. Advanced ones safeguard against malicious bots and data breaches while still facilitating faster website delivery.
Why is CDN Important For Website Speed?

A CDN is important for improving website speed because it delivers content faster to various locations. Here is why CDN is important for website speed:
Less Latency
A CDN stores content nearby to the user, which means that data doesn’t have to travel to various users’ locations. This makes the site load fast, reducing the delay or latency of the content load.
Quick Access to Heavy Media
Websites’ load can be slow due to many heavy videos, images, and graphics. A CDN helps it load fast by caching the content, making it instant access to the heavy media.
Dealing with Traffic Spikes
Websites often crash because their servers are too busy during product launches, flash deals, or viral events. The global server network of a CDN balances the traffic, which maintains the fast loading speed of a website.
Mobile Optimization
As mobile users are more widespread all over the world, a CDN can improve mobile website speed & performance significantly and provide the best experience possible to every user, no matter where they are.
Thus, CDN is important for reducing latency, speeding up load times, and ensuring faster, smoother browsing for users on any device or network.
What Are The Advantages Of A Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
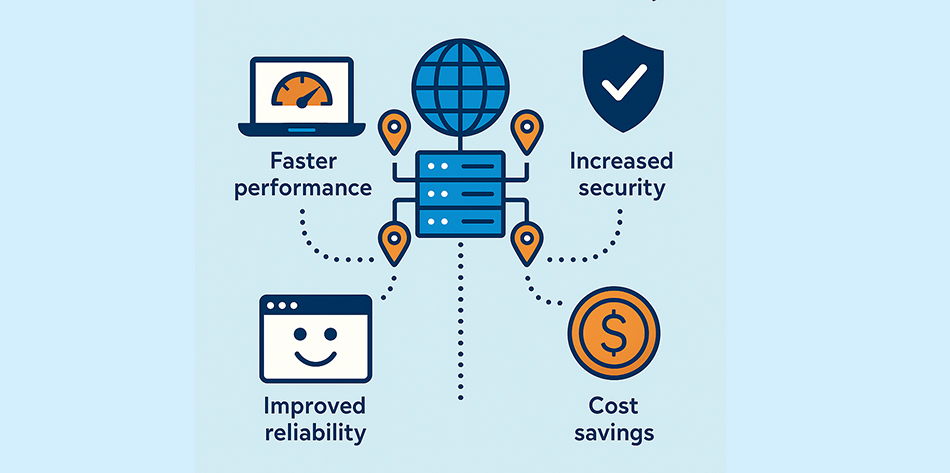
The CDN has a lot of benefits, especially for websites that receive higher traffic or serve people all over the world. Let’s take a closer look at the main benefits:
1. Faster Delivery of Websites
- Speed is the best advantage of a Content Delivery Network (CDN). Pages load in seconds because visitors obtain content from the server that is nearest to them. This keeps consumers interested for longer and lowers bounce rates.
- A study by Que-it says that even a one-second improvement in loading time can increase conversion rates by 5x in comparison to the one that loads in 10 seconds.
2. Increase Developer’s Efficiency
- A Content Delivery Network automates content delivery and caching, minimizing manual optimization tasks for developers.
- It enables faster testing and deployment, letting developers focus on new features instead of performance fixes.
3. Better Uptime and Dependency
- A CDN (Content Delivery Network) works by leveraging a network of servers all over the world. The traffic is automatically diverted to the next available server if one server goes down because of a technical problem or heavy traffic.
- This backup system makes sure that your site remains working even when things go wrong.
4. Less Server Load and Bandwidth Costs
- A CDN stores content on many servers across the world, which significantly minimizes requests to the origin server.
- Not only does this reduce the chance of server crashes during traffic surges, but it also lowers bandwidth costs because less data is sent from your hosting server.
5. Scalability Even in More Traffic
- CDN prevents crashes due to heavy load on the origin server and improves website loading by caching the website content, as your website traffic can touch the roof during sales, product launches, or viral spikes.
- With a worldwide server network, traffic is spread out among many edge servers, which keeps the site reliable and responsive.
6. Better Security
- Many Content Delivery Networks already have built-in security features like DDoS protection, SSL certificates, and firewalls.
- This not only protects your site from harmful attacks, but it also increases users’ trust as they feel safer when they visit a secure site.
7. Benefits for SEO and Rankings
- Google prioritizes speed of a website, user experience, and mobile performance to decide its rankings.
- Using a CDN to speed up your website also enhances its SEO exposure and ensures it performs better in Core Web Vitals.
8. Better Global Reach
- Websites that don’t use a Content Delivery Network may load quickly for people in your area but slowly for people from other countries.
- A CDN closes this gap by sending content through the closest global server network, ensuring that all users throughout the world get the same level of service
How Does CDN Improve Website Performance?
When we talk about performance, we don’t just mean speed. It is also about website efficiency, stability, and user experience. Here’s a more in-depth look at how a Content Delivery Network improves performance:
Lower Latency by Caching Content
- Latency is the time taken by the server to respond to a user’s request. A CDN lowers latency by storing static content on edge servers that are closer to the user.
- For instance, a person in Asia might obtain the identical data from a regional server in just 50ms instead of 300ms from a US server.
Improved File Delivery
- By distributing traffic across multiple servers, a CDN prevents bottlenecks, ensuring smooth, reliable delivery of images, videos, scripts, and other files even during high traffic.
- This makes your pages lightweight and ensures that your website loads faster without losing quality.
Better Experience for Users
- Users can have a smoother browsing experience on your website when the speed is consistent, and they will be less inclined to leave the site.
- Research shows that pages that load in less than two seconds attract more customers, increasing the chance of conversions.
High Availability and Load Balancing
- A Content Delivery Network (CDN) uses advanced load balancing to send requests to more than one server.
- If one edge server is too busy, the system quickly sends the traffic to the next best-performing server. This means that there will be less downtime and more dependability.
Better Streaming and Delivery of Heavy Files
- Websites that offer films, live streaming, or software downloads get a big boost from CDN benefits.
- By distributing large files throughout the global server network, buffering and interruptions are kept to a minimum, which ensures smooth playback and fast downloads.
Improving SEO and Core Web Vitals
- Performance metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Contentful Paint (FCP), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) have a direct effect on SEO.
- A CDN speeds up the delivery of content, which cuts down on rendering delays and helps you achieve Google’s Core Web Vitals standards.
Long-Term Performance Optimization
- As traffic around the world keeps going up, a CDN ensures your site can handle it.
- CDN ensures an enhanced site performance for the future as well.
Conclusion
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is one of the best methods to improve your website speed. By using a global server network and content caching, CDN delivers the website faster to every location.
With rising traffic and mobile users, you can improve website performance with a CDN to enhance user experience, speed, and SEO of your website. Implying CDN ensures a smooth user experience and lightning-fast website speed for the global audience.
FAQs
Q1: What does CDN mean?
CDN stands for "Content Delivery Network." It means a network of servers around the world that rapidly and efficiently sends cached website material to visitors.
Q2: Can a CDN help lower the demand on servers and the cost of bandwidth?
Yes. By caching content, a CDN cuts down on the number of requests sent to the origin server. This uses less bandwidth and puts less stress on the server.
Q3: How do I pick the best CDN for my site?
When choosing a CDN, think about things like where your target audience is, how much money you have, what features it comes with (like DDoS protection), and how well it works with your CMS or hosting provider.
Q4: What is the difference between web hosting and CDN?
Web hosting keeps your website's files safe and lets people access them online. A CDN (Content Delivery Network), on the other hand, speeds up delivery and performance by caching files and serving them from servers that are closer to users.
Q5: What does a CDN do to speed up websites?
A CDN cuts down on latency by sending content from the server that is closest to the user. This makes websites load faster, lowers bounce rates, and boosts SEO performance.